brom_drake Introduction 2 - "Drake-ify" My URDF
September 04 2024
TL;DR
One of the common hurdles that people encounter when trying to use
Drake is that their .urdf can not be loaded into the simulation.
Normally, this is because the .urdf file contains references to .stl and
.dae which Drake can not handle. There are 2 ways that you can use to fix this.
The first way is to use the brom_drake library to convert the .urdf file.
(I'll explain how to below.)
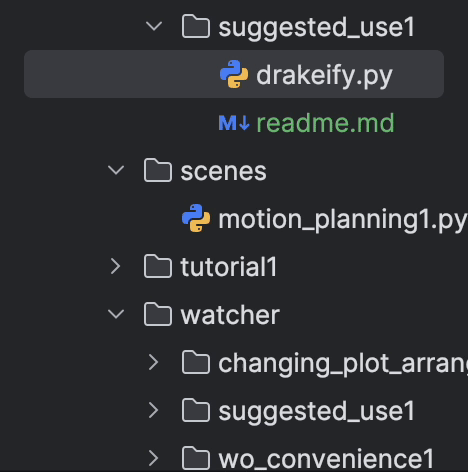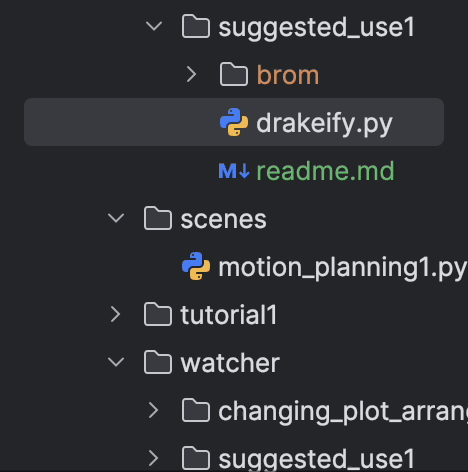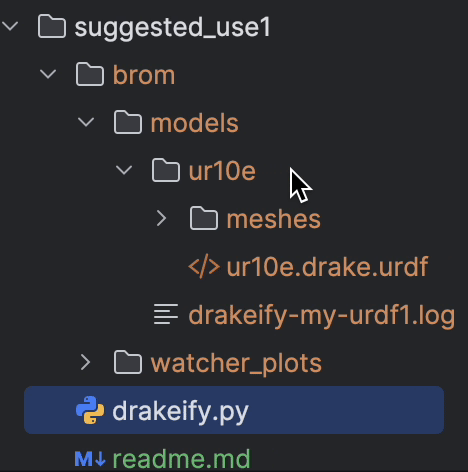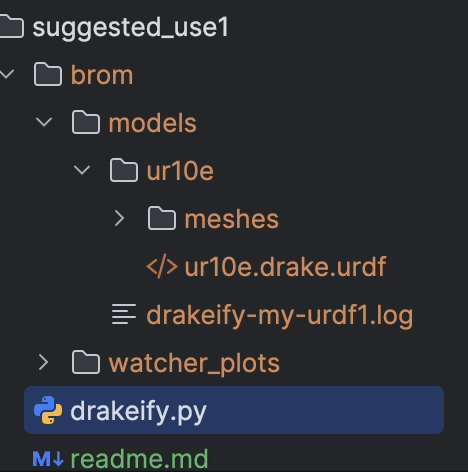
The convenience function drakeify_my_urdf() will convert your .urdf file into
a Drake-friendly .urdf file and it will be saved in the brom directory.
The second way is to:
-
Check that all "collision" geometries are Drake-ready files (e.g., are
.obj,.vtk, or.gltffiles).-
If they are not, then manually convert the
.stlor.daefiles into.objfiles using Blender or using a website like 3d-convert.com.
-
If they are not, then manually convert the
-
Verify that each of the actuated "joint" links in your
.urdffile has a transmission. (See this line from kinova_drake for an example transmission definition).- If you ever observe that your robot is successfully in the simulation but is not moving, then this is likely the issue.
To see a working example of brom's drakeify_my_urdf(), consider running
this script from the project.
Introduction
So, you've studied the documents, done a few tutorials and now are ready to create your OWN Drake simulation. You have all of the code written and you're ready to run it. But, when you run it, you get an error that says something like:
RuntimeError('MakeConvexHull only applies to obj, vtk, and gltf meshes; given file: **/brom_drake/robots/models/ur/meshes/ur10e/collision/base.stl.')
So, you need to convert ALL of the .stl and .dae files in your .urdf file
into one of the allowable formats: .obj, .vtk, or .gltf.
How do you do this?
Two Options: Brom Or GUI-Based Tools
Brom's newest feature is a one-line function (drakeify_my_urdf()) that will
take a target .urdf file and convert it into a .urdf file that Drake can handle.
By calling the function like so:
from brom_drake.all import drakeify_my_urdf
""" Your amazing code """
original_urdf_path = "path/to/your/original.urdf"
new_urdf_path = drakeify_my_urdf(original_urdf_path)
# Add the new URDF to your plant
plant, scene_graph = AddMultibodyPlantSceneGraph(builder, time_step=time_step)
added_models = Parser(plant=plant).AddModels(str(new_urdf_path))
""" More of your amazing code """
You will convert the .urdf file at original_urdf_path into a Drake-friendly
.urdf file and save it in the brom directory. From there, you can add the
model to drake using the standard Drake methods.
If that doesn't work for you, or you'd rather not use Brom, then you can use a GUI-based tool like Blender
to convert the .stl and .dae files into .obj files. Simply, download
Blender, open the .stl or .dae file, and then export it as an .obj file.
Similarly, you can use a website like 3d-convert.com
to convert the files.
Then, search through the code and manually verify that each of the actuated "joint" links
in your .urdf file has an accompanying transmission element. See this file for more examples.
If you would like more information on how to use Brom or have a suggestion for what we should build next, then let me know!